Bauxite is the main resource to make aluminum
Although aluminum is the most common metal we see in our daily life, accounting for 8% of the planet's crust, the metal is too reactive with other elements to occur naturally.
Bauxite, a rock formed from a reddish clay material call laterite soil, is the primary resource of aluminum and is usually found in tropical or subtropical areas.
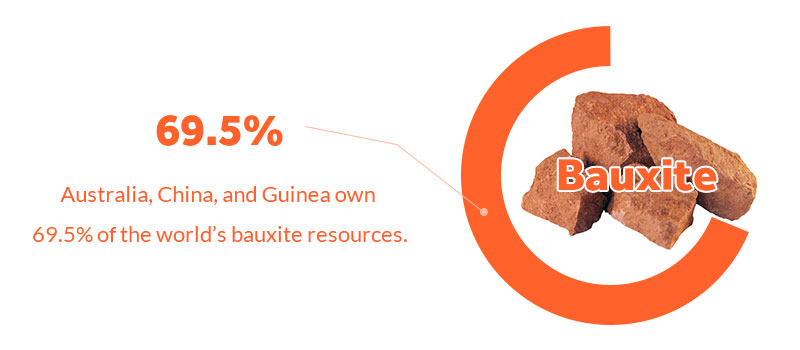
According to data of global bauxite resources reservation, the world's largest bauxite producers are Guinea, Australia, Vietnam, Brazil, Jamaica, Indonesia, China, India, Russia, and Malaysia, among which, Australia, China, and Guinea own 69.5% of the world's bauxite resources.

Bauxite forms near the surface thus the best way to mine it is through open-pit mining. The bauxite mining industry plays a leading role in environmental protection.
During the bauxite mining process, cleaning and storing the surface earth are the first things to do for earth restoration. If mining in the forest area, you'll see that 80% of land can restore to its native ecosystem.
How to extract aluminum from bauxite-Bayer process and all-Héroult process?
Bauxite is mainly composed of alumina, silica, iron oxide and titanium dioxide. Around 70% of bauxite ore in the world adopts Bayer process to produce alumina. Then by Hall-Héroult electronic process, alumina can be reduced to pure aluminum.
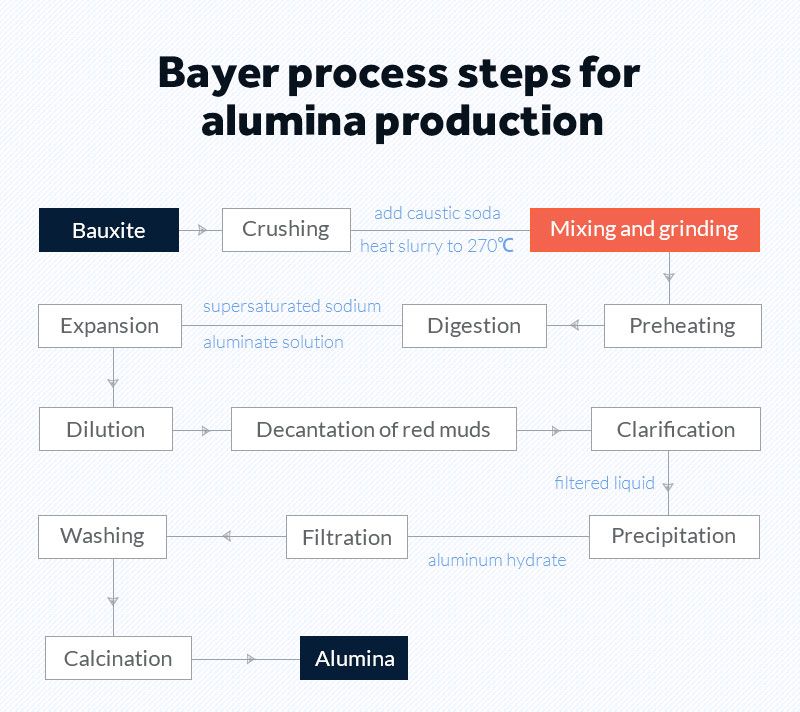
Bayer process steps for alumina production
As the bauxite is found near the surface, it needs an open-pit mining.
Step 1- Crushing process
The first step of the Bayer process is to use the crushing equipment to crush the bauxite ore into particles with a diameter of about 30 mm. As the particle size becomes smaller, the specific surface area of the bauxite greatly increases, which helps to speed up the follow-up speed of the chemical reaction.
Step 2- Washing and separating processes
After being crushed by crushers, the bauxite needs a sand washing machine to remove and separate the clay and impurities on the particle surface. If did not experience washing process, bauxite with high content of SiO 2 would occur fouling and end product quality problems.
Step 3- Grinding and mixing processes
After washing process, the bauxite particles mix with a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 30%-40%, which then forms a suspension with a solid particle size below 300 microns under the help of a ball mill. The bauxite and the caustic soda returned from the precipitation stage are added in the mill to make pumpable slurry.
Underground the above processes- washing, crushing, grinding, the bauxite particles are reduced to increase the available surface area for the digestion stage.
Step 4- Digestion process
In the digestion process, the slurry is heated to 270℃ to form a sodium aluminate supersaturated solution or "pregnant liquor". A hot caustic soda (NaOH) solution can dissolve the aluminium-bearing minerals in the bauxite.
There are two types of bauxite: gibbsite, böhmite and diaspore.
Gibbsite:
Al(OH)3 + Na+ + OH- → Al(OH)4- + Na+
Böhmite and Diaspore:
AlO(OH) + Na+ + OH- + H2O → Al(OH)4- + Na+
Conditions within the digester (caustic concentration, temperature, and pressure) are set according to the properties of the bauxite ore. If bauxite ores have high gibbsite content, it needs to be processed at 140°C. The other type of bauxite ore- böhmitic bauxites require temperatures between 200 and 280°C.
The pressure in the digestion process is not important but is determined by the steam saturation pressure. At 240°C the pressure is approximately 3.5 MPa. The slurry is then cooled in a series of flash tanks to around 106°C.
The digestion process can maximize the alumina recovery rate and liquid production rate in the bauxite.
Step 5-Clarification process/ settling process
Bauxite residue settles at the bottom and is washed and filtered prior to disposal. The first thing to do in the clarification process is to separate the bauxite residue from sodium aluminate remains in solution through sedimentation.
Then using a series of Security filters to further separate pregnant liquor from the bauxite residue. The purpose of the security filters is to ensure that the final product is not contaminated with impurities present in the residue.
Step 6- Percipitation Process
The filtered liquid is cooled down and treated with seed crystals, which help crystalisation forminig aluminium hydrate.
In the precipitation process, the polished filter is used to remove the particles in the water for further control of the iron elements.
When liquid that needs to be filtered goes down, the specific fine-grained inert filter media bed can relocate the particles through constant water injection by slowly rotating the spray arm. In this stage, the alumina is recovered by crystallisation from the pregnant liquor, which is supersaturated in sodium aluminate.
The precipitation reaction is the reverse of the gibbsite dissolution reaction in the digestion stage:
Al(OH)4- + Na+ → Al(OH)3 + Na+ + OH-
Step 7- Calcination process
Alumina hydrate is heated to 1100℃ to remove the bonded water molecules, producing aluminum oxide. There are different calcination technologies in use, including gas suspension calciners, fluidised bed calciners and rotary kilns.
The following equation describes the calcination reaction:
2Al(OH)3 → Al2O3 + 3H2O
Alumina is a white powder, and the final product of the Bayer process.
Hall-Héroult electrolysis process produces aluminum
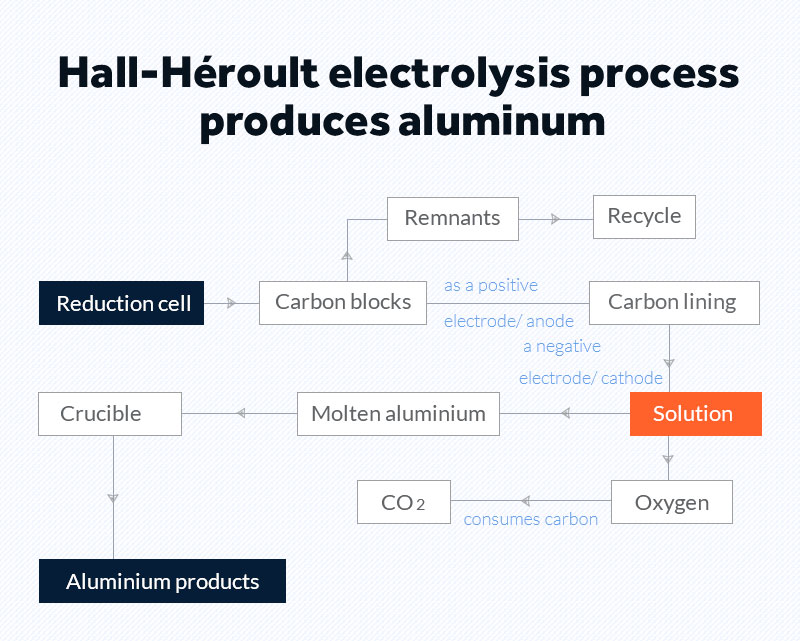
After Bayer process, alumina is converted into molten aluminum through the Hall-Héroult process which happens inside a series of electrolytic reduction cells.
The electrolytic reduction cell includes cryolite-based electrolyte, aluminum feeder, carbon block, and carbon lining. Aluminum smelting requires large amounts of electricity.
- 1Carbon blocks are manufactured and get consumed in the process, but remnants are recycled and reused.
- 2The act as a positive electrode, or anode, and the carbon lining becomes a negative electrode, or cathode.
- 3As electricity passes through the solution, an electrolytic reaction happens, and it breaks alumina into hot molten aluminium and oxygen.
- 4Oxygen consumes carbon from the anode forming CO2.
- 5Hot molten aluminium is accumulated to the bottom of the cell because of high density, and it is then trapped by a crucible.
- 6Crucibles with molten aluminium are transported to the casthouse to make the final products.
During the process, alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite (Na 3 AlF 6) to lower its melting point for electrolysis. Finally, the electrolytical reduction at a temperature of about 960°C produces 99.5-99.8% pure aluminum. The molten aluminium is then cast using different technology.
The molten aluminium is cast with different technology

Aluminum products are widely used, from cars, smart phones to skyscrapers. But aluminum also forms alloys with elements such as silicon, magnesium, and copper to create special properties required for certain applications.
Liquid aluminum and other elements are mixed and heated with electromagnetic stirring technology in the furnace. Different technologies are used to cast molten aluminum to produce the required aluminum products.
Sow casting
In sow casting liquid metal is poured directly into a mould and allowed to solidify. these products are re-melted for use in electronics and the aerospace industries.
Open mould ingot casting
Ingots are used to produce car wheels, car engine blocks and other automotive parts.
Sheet ingot casting
Sheet ingots are rolled into flat products that are used in packaging, the automotive industry and lithography.
Billet ingot casting
The material is heat-treated inside a chamber, and then chilled to achieve the required material properties. billets are used in the automotive, construction and aerospace industries. Bauxite is the best and only material for manufacturing aluminum metal.
In addition, bauxite is also widely used in the chemical industry, refractory bricks making, abrasives making, cement making, steel manufacturing, and petroleum fields. Laterite bauxite is commonly used as a building material.
Calcined bauxite made of high-alumina sintered at high temperature in a rotary kiln is used as a non-slip road aggregate for preventing road accidents.
Common problems about aluminum production
How much is bauxite needed to make aluminum and how much power is required?
It is estimated that the production of 2 kg of alumina requires 4 kg of bauxite, consumes about 8 kilowatts of electricity, and produces 1 kg of pure aluminum.
What chemical is used to go from bauxite to aluminum?
Concentrated sodium hydroxide
What useful material may be obtained from bauxite?
Bauxite is a mixture of hydrated alumina, aluminum hydroxide, clay minerals, and insoluble materials such as quartz, hematite, magnetite, siderite, and goethite. The aluminum minerals in bauxite include: gibbsite Al(OH) 3, boehmite AlO(OH) and diaspore AlO(OH).