With growing global emphasis on green manufacturing, the need for efficient and eco-friendly sand dryers has become more important than ever.
This blog explores the industrial benefits of sand drying, the sand materials that can be dried using a sand dryer, the drying process, and the applications of sand drying plants in the United States and Mexico.
Why is it important to dry sand?
In industries like construction, concrete, and cement manufacturing, high-quality dry sand is a crucial ingredient.
Sand often arrives with varying degrees of moisture due to natural or processing factors. Drying sand is not just about removing water—it significantly improves the usability, storage, and performance of the sand in many industries.
1. Enhanced material handling
Wet sand tends to clump and stick together, which complicates transportation and storage. Dry sand flows freely and can be handled with conveyors or hoppers more efficiently.
2. Improved product quality
In construction, for example, moisture-laden sand can weaken concrete and mortar mixes. Dry sand ensures better bonding with cement and reduces the risk of cracks or structural issues.
3. Essential for industrial use
In glass manufacturing, foundry casting, and hydraulic fracturing, moisture must be precisely controlled. For instance, foundry sand must be completely dry to prevent steam explosions during metal pouring, while frac sand needs to flow freely under high pressure.
4. Lower transport costs
Moisture adds weight. By reducing the water content, sand becomes lighter, resulting in lower transportation and shipping expenses.
5. Energy efficiency in further processing
For operations like calcination, melting, or chemical treatment, starting with dry sand reduces energy consumption and processing time.
What sand materials can be dried?
Sand dryers—especially rotary sand dryers—are highly versatile in multiple industries. They can effectively dry wet sand and similar aggregate materials.
Sand is mainly composed of minerals such as quartz and feldspar, and the particle size ranges from 0.0625 mm (fine sand) to 2 mm (coarse sand).
Sand that can be dried Is divided into natural sand and manufactured sand (M-sand). Natural sand is mostly formed in rivers, beaches, deserts, and lakes. However, M-sand is the artificial sand that is mostly made of the curshing and sand making process of rocks and minerals.

Here are the most common types of sand materials:
- Natural sand (such as river sand, beach sand, sea sand, etc.)
- Rock sand (such as granite sand, basalt sand, etc.)
- Mineral sand (such as garnet sand, dolomite sand, chromite sand, calcite sand, quartz sand, silica sand, etc.)
- Construction sand
- Manufactured sand (M-sand)
- Foundry sand
- Frac sand
- Mortar sand
- Green sand
- White sand
These sand materials often contain moisture ranging from 5% to 25%, which must be reduced to 0.5%–1% depending on the end-use sand and aggregate drying requirements. A rotary sand dryer is specifically engineered to handle such moisture levels while ensuring consistent drying results.
How to dry sand?
The sand drying equipment is the core equipment for sand drying. However, the entire sand drying process also requires a lot of auxiliary equipment, such as belt conveyors, heating furnaces, fans, temperature control systems, drive devices, dust collectors, etc.
1. Understand the sand dryer structure
Sand is usually dried in a single drum rotary dryer. This is a popular type of rotary dryer, also known as a single pass dryer. It is famous for its simple structure, easy installation and maintenance, and good sand drying effect.
The single drum sand dryer consists of the following key parts:
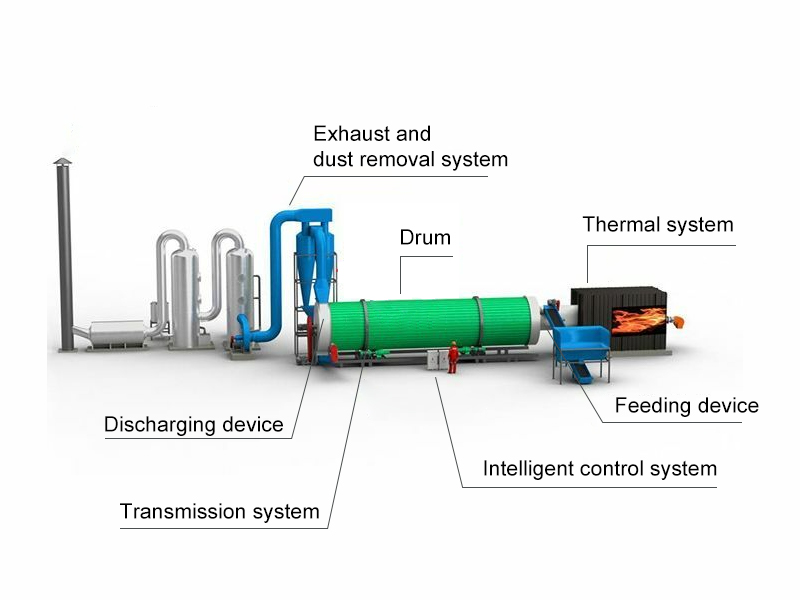
- Feeding device: Wet sand is loaded via a conveyor, hopper, or feeder that ensures smooth, controlled input without clumping or blockages.
- Drum: A long rotary drum—single pass—rotates slowly, lifting and tumbling the sand through a hot air stream using internal flights (lifting plates). This maximizes contact between air and material for fast, uniform, and non-stick drying.
- Thermal system: A direct or indirect-fired burner produces hot air (typically 300°C–800°C) that removes moisture from the sand. Heat sources or fuels may include gas, diesel, coal, or biomass.
- Transmission system: Electric motor and gear units rotate the drum at controlled speeds to manage residence time and throughput. Discharging device: Dried sand exits via a conveyor, ready for screening, storage, or packaging.
- Exhaust and dust removal system: This system prevents air pollution and has a dust removal efficiency of up to 99.99%.
- Intelligient control system: Real-time sensors monitor and control temperatures, moisture, and airflow. The intelligent PLC system allows automatic adjustments for optimal performance.
2. Start-up procedure
- 1Power on the drying system and check all connections.
- 2Ignite the burner to begin heating.
- 3Choose a heating method: Direct drying heats sand with hot air or gas for higher efficiency, while indirect drying uses a heated surface without direct contact.
- 4Set the temperature (typically 80°C–200°C at the inlet).
- 5Start the drum rotation at a preset speed (RPM depends on dryer size).
- 6Turn on the feeding system to begin introducing wet sand.
3. Sand drying process
In a complete sand drying plant, how does a sand dryer work?

As the drying drum rotates, sand is lifted by internal flights and cascades through the hot air stream.
- Heat is transferred from the air to the sand via convection, evaporating moisture.
- The drum's gentle slope moves sand toward the discharge end as it dries.
- The moisture content is gradually reduced from typically 10–12% down to 0.5%–1% or less.
- Dried sand exits at the discharge end, then is stored in silos, hoppers, or directly packed.
The modern sand drying plant offers the intelligent control system to ensure efficient and safe sand production. Here are the sand drying process parameters:
| Parameters | Description |
| Drying Temperature | Adjustable based on sand type and moisture, typically 80°C–200°C. For example, river sand is 80°C–180°C |
| Final Moisture | Can be reduced to 0.5%–1% |
| Capacity Range | 1.9–76 tons per hour, short drying time |
| Heating Method | Direct or indirect heating options. Direct heating is much more popular |
Customer cases about sand drying
1. Sand drying plant in the United States
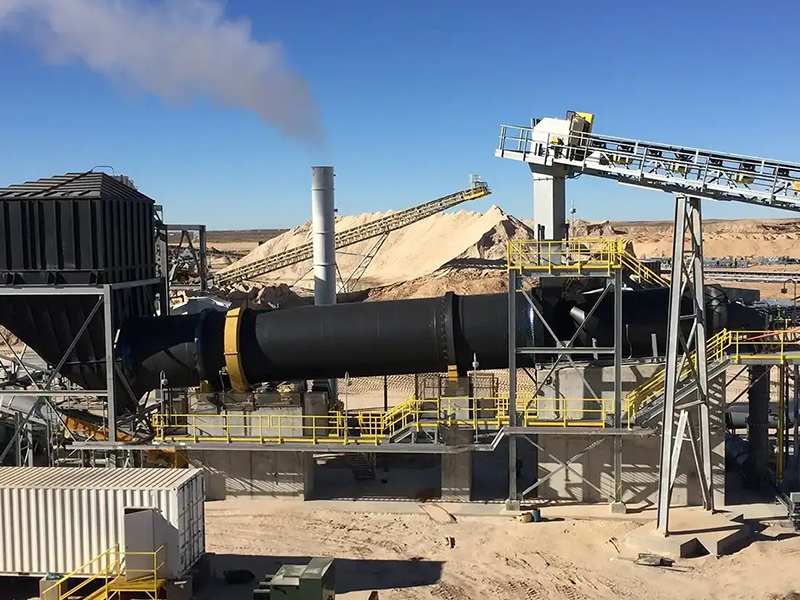

Project information
- Client: A concrete aggregate supplier
- Dried material: River sand and construction sand
- Problem: High natural moisture content affected batching precision and slowed project timelines.
- Solution: A complete rotary sand drying plant was installed, equipped with 30 TPH capacity rotary drum dryer, natural gas burner, pulse dust collector, automated feeding and discharge system.
- Final moisture: reduced from 12% to 0.5%
- Energy savings: 25% lower than the previous system
Customer feedback:
The output sand was directly used in batching plants for high-performance concrete mixes.This sand drying plant has improved the concrete quality and reduced material waste. The client reported faster mixing cycles and higher profitability due to better control over moisture levels.
3. Silica sand slurry drying plant in Mexico
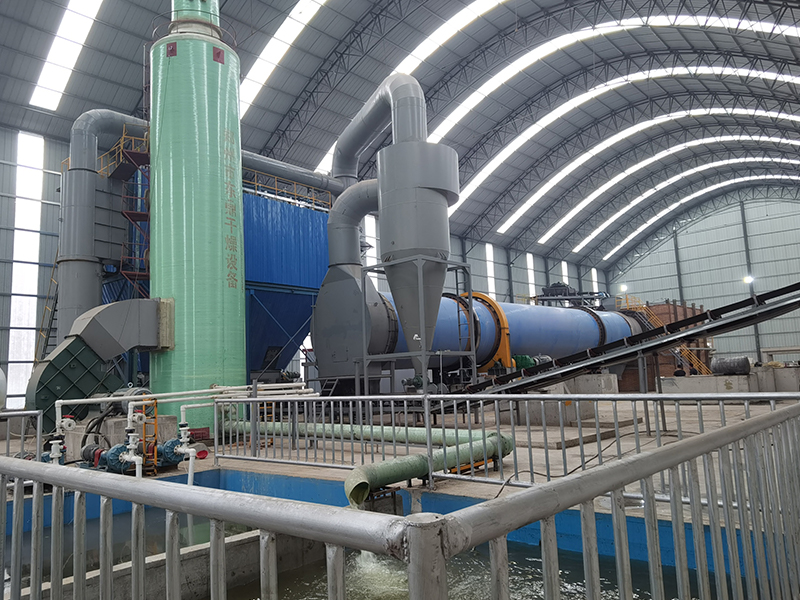

Project information
- Client: Mining and construction material company
- Material: Wet silica sand slurry from tailings
- Problem: The company needed to convert a high-moisture sand slurry into fine, dried powder suitable for export and reuse in cement blends.
- Solution: Custom-designed rotary sand dryer with pre-dewatering system, with the capacity of 50 tons per hour, advanced temperature control system, filter baghouse to meet local environmental laws.
Customer feedback:
The company successfully turned waste slurry into a profitable product. The final moisture is 1%. The dried sand powder is now used as a cement additive, contributing to greener construction materials.
Conclusion
As construction and cement industries face increasing demand for eco-friendly dry sand, modern sand dryers—especially rotary sand dryers—play a critical role in sustainable material processing.
Whether you are drying silica sand or producing dry construction sand aggregates, an advanced sand drying plant can help you meet quality standards, cut costs, and align with the green goals of today’s building industry.