Lead and zinc are relatively important non-ferrous metals, often coexisting to form polymetallic deposits. Lead-zinc ore is a kind of mineral resource rich in lead and zinc.
In nature, there are about 250 types of lead-zinc minerals discovered, of which about 1/3 of the minerals are sulfides and sulfates. Sphalerite and galena are the most important and are the main industrial raw materials for smelting zinc and lead.

Mineral testing of lead-zinc ore
Lead-zinc ore is mainly composed of lead and zinc minerals, gangue minerals (such as calcite, quartz, dolomite, mica, feldspar), and other metals (such as pyrite, chalcopyrite). Lead-zinc deposits are usually processed into concentrates, and lead-zinc metal products are smelted.
Different beneficiation processes are selected according to the different types of lead-zinc ore.
- Sulfide lead-zinc ores: Usually by flotation.
- Oxide lead-zinc ores: Use flotation method, or gravity separation before flotation, or gravity first and sulfuric acid treatment, and then flotation.
- Mixed lead-zinc ores: The combined beneficiation method is generally used for lead-zinc ores containing multiple metals.
Before designing the lead-zinc ore beneficiation process for customers, Ftmmachinery can conduct ore beneficiation tests and configure related beneficiation equipment.
Contact us for a Free Sample Testing!
Lead-zinc ore beneficiation flow
The beneficiation process of lead-zinc ores generally goes through 4 stages: crushing, grinding, separating, and drying.
Stage 1: Lead-zinc ore crushing
Two-stage and one closed-circuit crushing is currently the most widely used crushing process in lead and zinc concentrators.
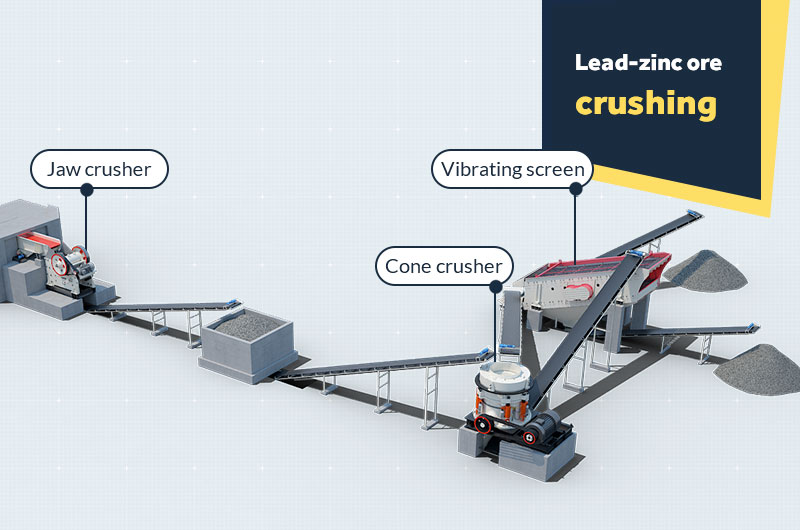
- 1Coarse crushing: Raw lead-zinc ores pass through the vibrating feeder, enter the jaw crusher for coarse crushing, and then send them to the cone crusher.
- 2Fine crushing: The lead-zinc ores are finely crushed in the cone crusher, and the ore particle size generally reaches 0-15 mm. After that, they are sent to the vibrating screen, and the ores that do not meet the specifications are returned to the cone crusher for crushing, forming a closed-circuit process.
Some large and medium-sized lead-zinc plants also use a three-stage closed-circuit crushing process, and the output particle size can reach 0-5 mm.
Stage 2: Lead-zinc ore grinding

- 1Grinding: The lead-zinc ores of 0-15mm are evenly sent to the ball mill for grinding.
- 2Classification: After grinding ores, the spiral classifier controls the classification, which can also play the role of washing.
For lead-zinc ores with grinding particle size above 0.15 mm, the one-stage grinding process is adopted. For large concentrators, when the grinding fineness is required to be below 0.15 mm, the two-stage grinding process is adopted. The content of -200 mesh can reach 70%-80%.
Stage 3: Lead-zinc ore separating
According to the mineral test, it can be seen that the beneficiation of lead-zinc ores is mainly based on gravity separation and froth flotation.
Gravity separation method of lead-zinc ore
Gravity beneficiation is a commonly used method for lead-zinc mines. For coarse-grained or aggregate disseminated lead-zinc ores, heavy medium separation is adopted to discard a large amount of gangue and surrounding rock waste.
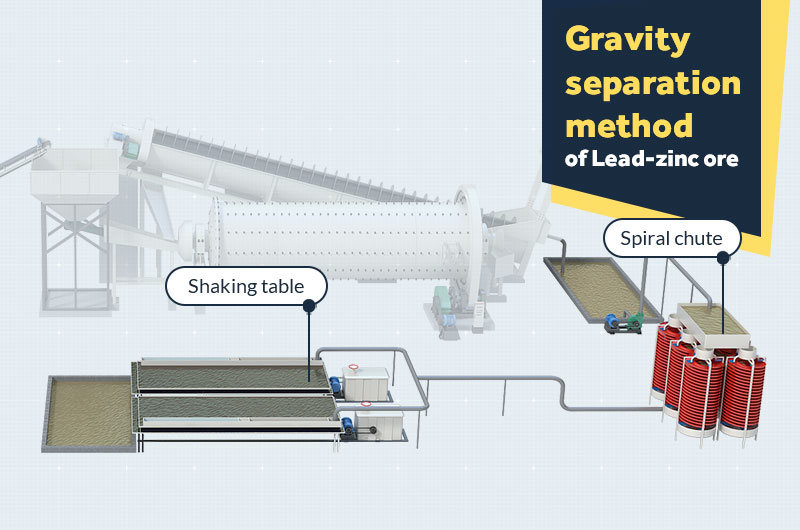
- 1Rough separation: The classified lead and zinc ores are sent to the spiral chute for heavy medium separation. The coarse concentrates obtained with a single helical chute have a lower grade.
- 2Re-election: If you want to obtain higher-grade lead-zinc concentrates, you can use the shaking table again for enrichment.
In addition, lead-zinc ores can also be separated by gravity using a jig.
Flotation method of lead-zinc ore
Lead-zinc ores concentrated by froth flotation are an important process. For fine-grained ores with complex intergrowth, the flotation process can achieve an ideal separation effect, effectively recovering low-grade ores.
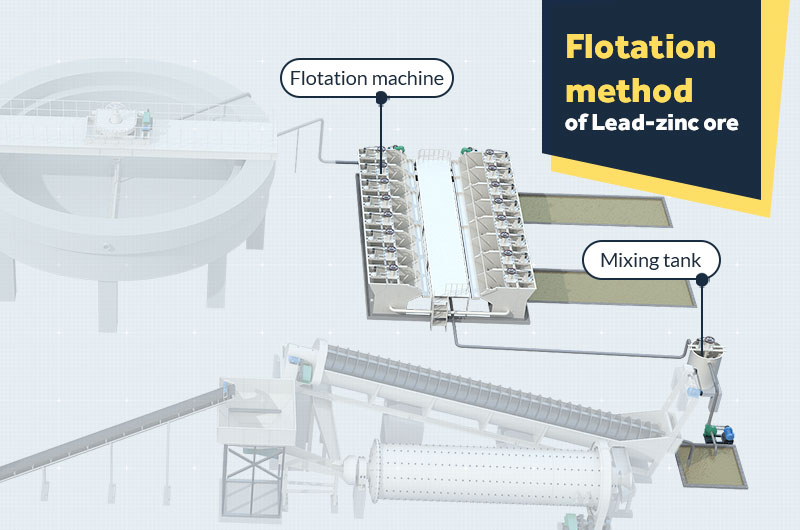
- 1Mixing: The lead-zinc minerals are sent to the mixing tank for stirring, and control the pulp concentration at 25-35%. Add flotation agent, control the pH value of pulp to 9-11, and stir for 6-15 minutes.
- 2Flotation: The process is to suppress zinc floating lead, and then activate zinc. According to the floatability of the ores, lead concentrates, zinc concentrates, and tailings are obtained by froth flotation in sequence.
If you want to obtain higher grade lead and zinc concentrates, the whole process can go through roughing, secondary and tertiary flotation.
Stage 4: Lead-zinc ore drying
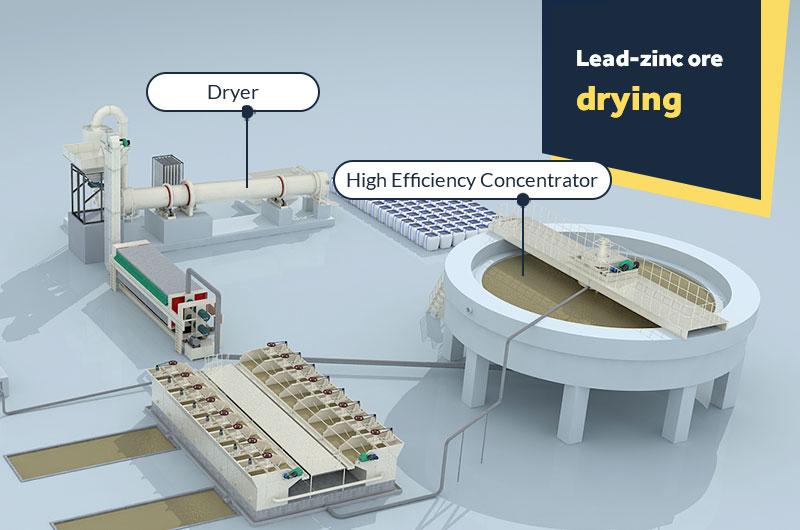
- 1Concentration: The concentrates after flotation or gravity contain certain moisture, which needs to be concentrated and precipitated in the high-efficiency thickener.
- 2Drying: The lead and zinc concentrates are then dried and dehydrated by the dryer to obtain finished products.
Features and case of lead-zinc ore gravity separation
Gravity separation features of lead-zinc ore
Process advantages
- Large production capacity, low beneficiation cost, and long machine life;
- Effectively remove gangue from lead-zinc ore and increase the content of useful components;
- Desliming can be carried out when the lead-zinc ore is clay-like;
- The whole process uses circulating water, which does not pollute the environment.
Process disadvantages
- Gravity method is difficult to separate raw ores with fine particle size and low density;
- Lead-zinc ore gravity separation is mostly used for pre-enrichment.
Lead-zinc ore gravity separation in Australia Free Customized Design
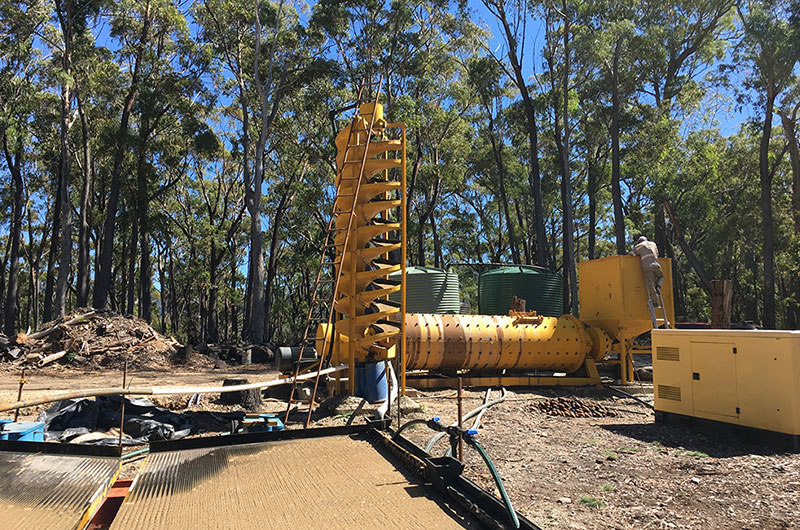

Ftmmachinery lead-zinc ore gravity separation case in Australia
A lead-zinc mine in Australia is mainly composed of three sulfide minerals: galena, sphalerite, and pyrite. Among them, the content of sphalerite is the most. The mineral composition of the ore is as follows:
| Minerals | Galena | Sphalerite | Pyrite | Gangue |
| Low grade | 1.8 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 84.1 |
| Middle grade | 3.2 | 11.6 | 4.6 | 80.6 |
| High grade | 4.2 | 14.7 | 3.6 | 77.6 |
Through the heavy medium separation process, 41.55% of floating ores can be discarded in advance, which effectively improves the grade of selected ores. Finally, the sinking lead-zinc ores with a yield of 58.45% can be obtained.
The grade and recovery rate of lead and zinc are as follows:
| Minerals | Lead | Zinc |
| Grade of raw ore | 1.77% | 4.15% |
| Grade of concentrate | 2.92% | 6.50% |
| Recovery rate | 96.5% | 91.5% |
Features and case of lead-zinc ore flotation
Flotation features of lead-zinc ore
Process advantages
- Good separation effect and high quality for refractory lead-zinc ores;
- Flotation method can realize the separation of lead and zinc, improving the content of lead and zinc;
- Flotation process is energy-saving and high-yield. The energy-saving can reach 60% and the recovery rate is increased by 1%-5%.
Process disadvantages
- Large equipment investment and high production cost;
- Various reagents added in the flotation of lead-zinc ore are harmful to the environment.
Lead-zinc ore flotation in Peru Free Customized Design
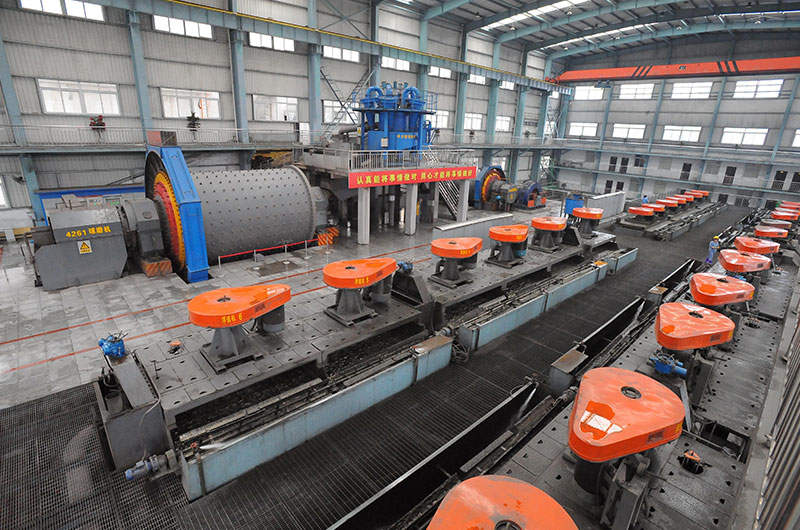

Ftmmachinery lead-zinc ore flotation case in Peru
The main minerals of a lead-zinc mine in Peru are 5.1% galena and 15.0% sphalerite. The ores are characterized by a high lead-zinc oxidation rate (10-30%) and a large amount of easy-floating pyrite (20-30%). The mineral content is as follows:
| Minerals | Lead | Zinc | Iron |
| Content | 3.94% | 7.23% | 17.85% |
Change the traditional flotation sequence of lead, zinc, and sulfur, so that pyrite is better than sphalerite, and floats together with galena. And then lead and sulfur are separated.
The recovery rate of lead and zinc are as follows:
| Minerals | Lead concentrate | Zinc concentrate |
| Grade | 62.07% | 42.71% |
| Grade of concentrate | 2.92% | 6.50% |
| Recovery rate | 76.31% | 73.06% |
Focusing on investment cost and comprehensive utilization of minerals, Ftmmachinery has improved the flotation process and proposed the selective flotation of lead and zinc. With the concentrate grade unchanged, the total recovery rate of lead and zinc has increased by nearly 3%.